
Research Assistant is an AI-enabled tool in MultiSearch that allows you to search the Macquarie University Library catalogue using natural language queries. You can use Research Assistant to:
How to access Research Assistant

More information about MQ Library Research Assistant can be found from below guide:
Research Rabbit is a free research platform that enables you to discover and visualise relevant literature and authors, create alerts for newly published papers and share collections with colleagues.

Consensus is a search engine powered by AI in scientific research. It uses Semantic Scholar data and synthesize both topic-level and paper-level insights.
Key Features of Consensus:
Consensus uses OpenAI’s GPT-4 model to generate a one-sentence summary of the top 10 studies. For yes/no questions, a custom model classifies results as “yes,” “no,” or “possibly,” shown in the Consensus Meter, which displays a distribution of supporting and contrasting evidence.

For papers that have full-text PDFs, you can use the built-in chatbot to ask questions about these papers.
Elicit is an AI tool to assist in searching, screening and summarizing literature. It is especially useful for empirical research like randomised controlled trials. After entering a research question, Elicit will display relevant papers and summaries of key information about those papers in an easy-to-use table. The steps are:

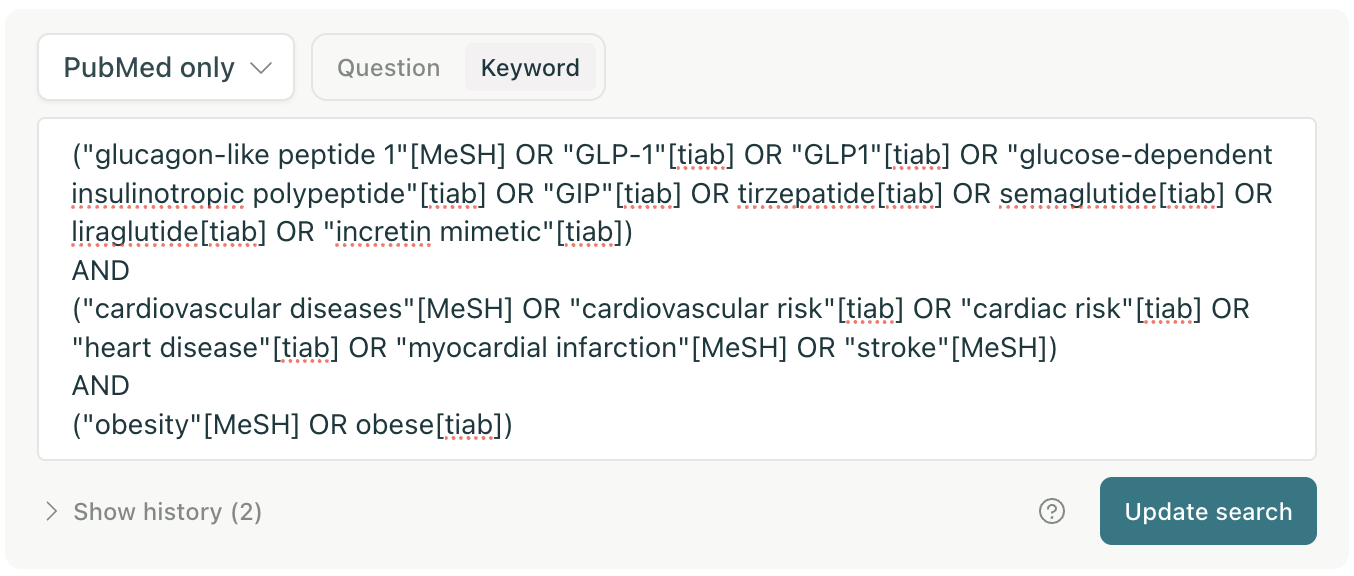
8. Newly released keyword search in Elicit Systematic Reviews for Pro, Teams, and Enterprise users, can build strong keyword queries from plain language research questions, and search papers across PubMed, ClinicalTrials.gov, and the Elicit paper bank in a reproducible, transparent way.
Scite is a tool which offers a quantitative and qualitative insight into how publications cite each other. It has 1.2 billion citation statements extracted and analysed from 181 million articles, book chapters, preprints and datasets. It accesses full text articles and uses a deep learning model to tell you
Scite users can
SciSpace/Typeset is an AI-powered research platform with tools to discover, explore, understand, and write research, which includes below key features:
Connected Papers is a visual tool to help researchers find and explore papers relevant to their field of work.
Inciteful has developed two tools to date
Litmaps generates an interactive map of relevant articles that relate to a seed paper. The most recent articles appear on the right hand side of the map, the most cited articles appear at the top and the lines show the citations in-between. Users can click on each dot and add more concepts to expand the map.